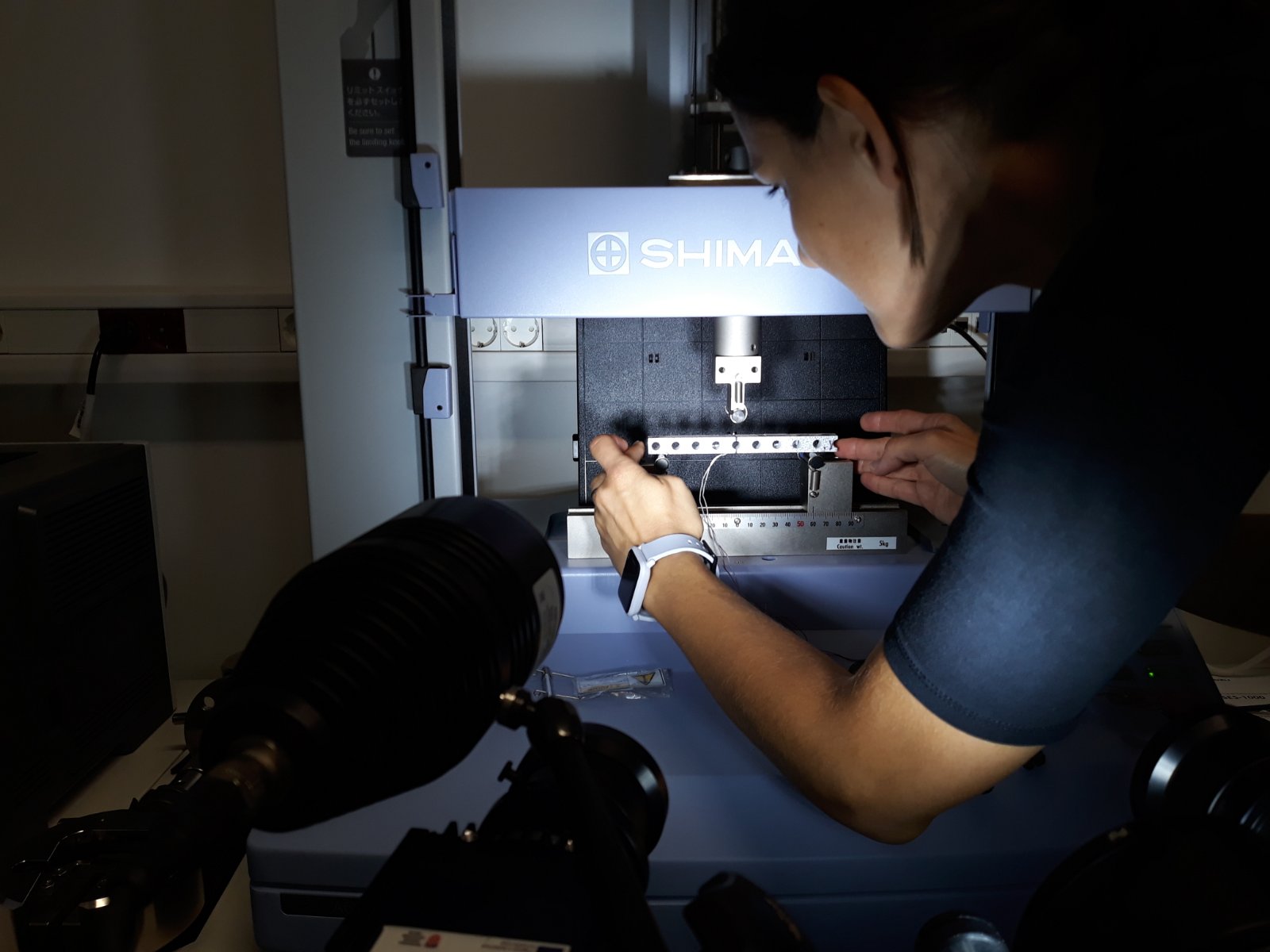
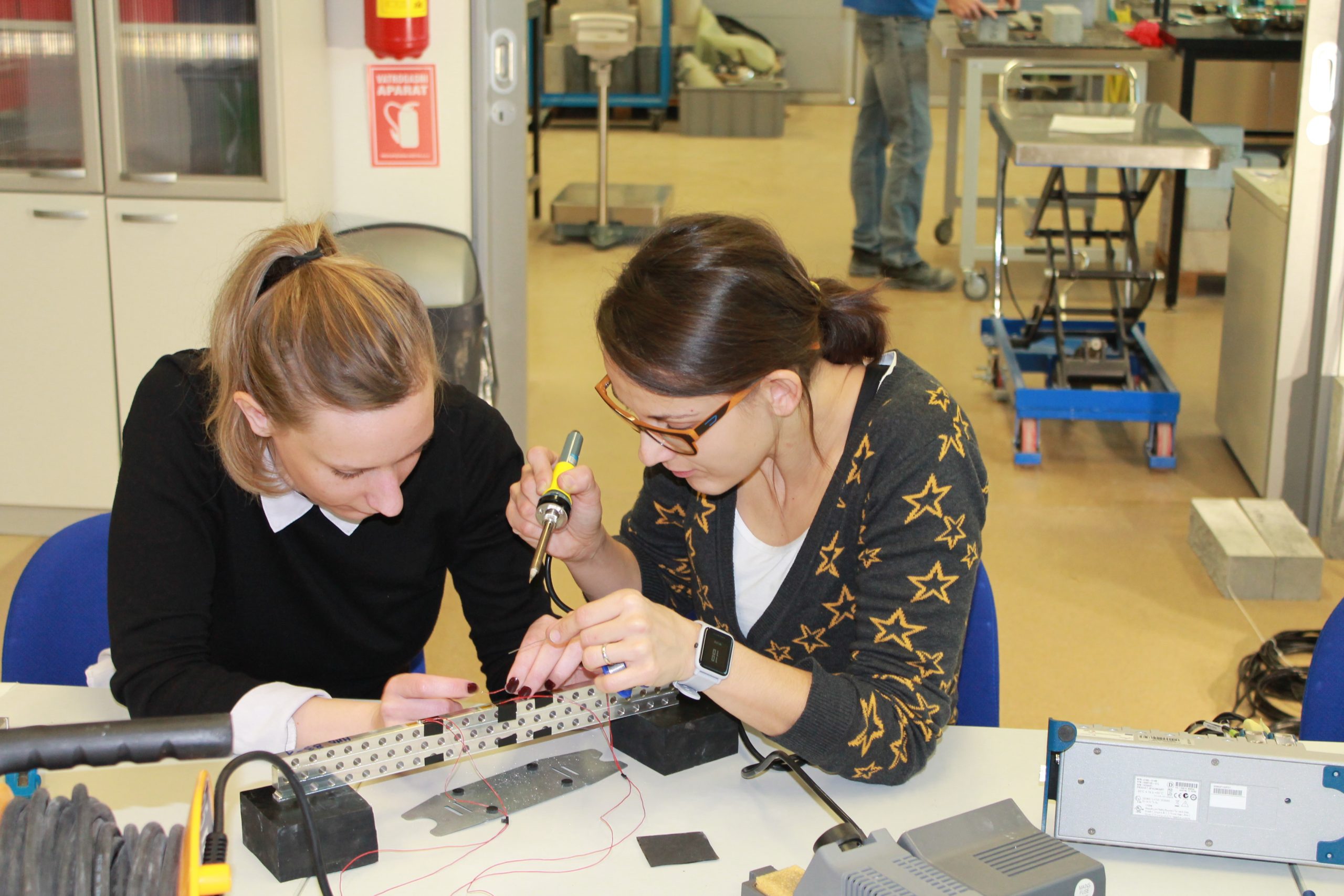
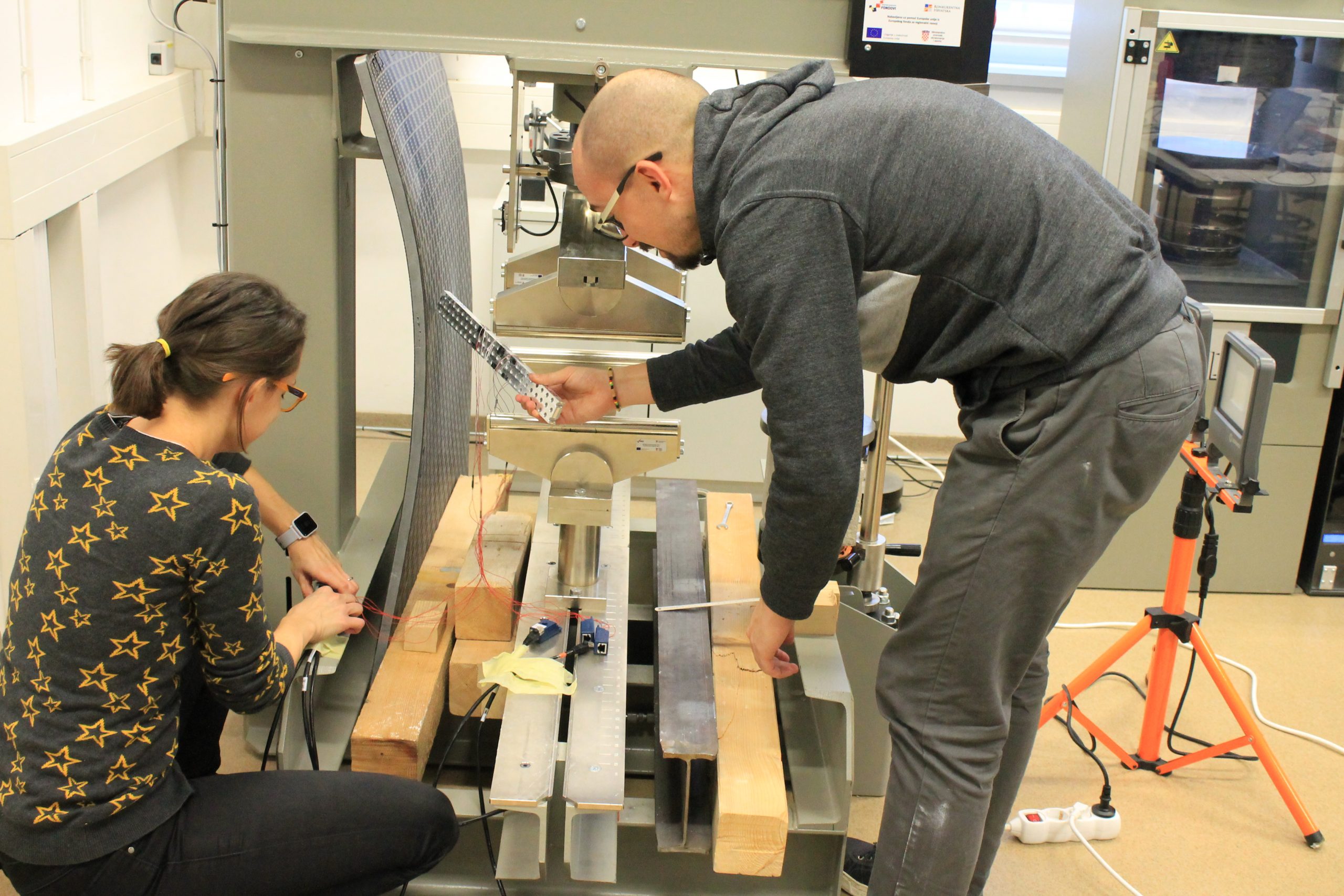
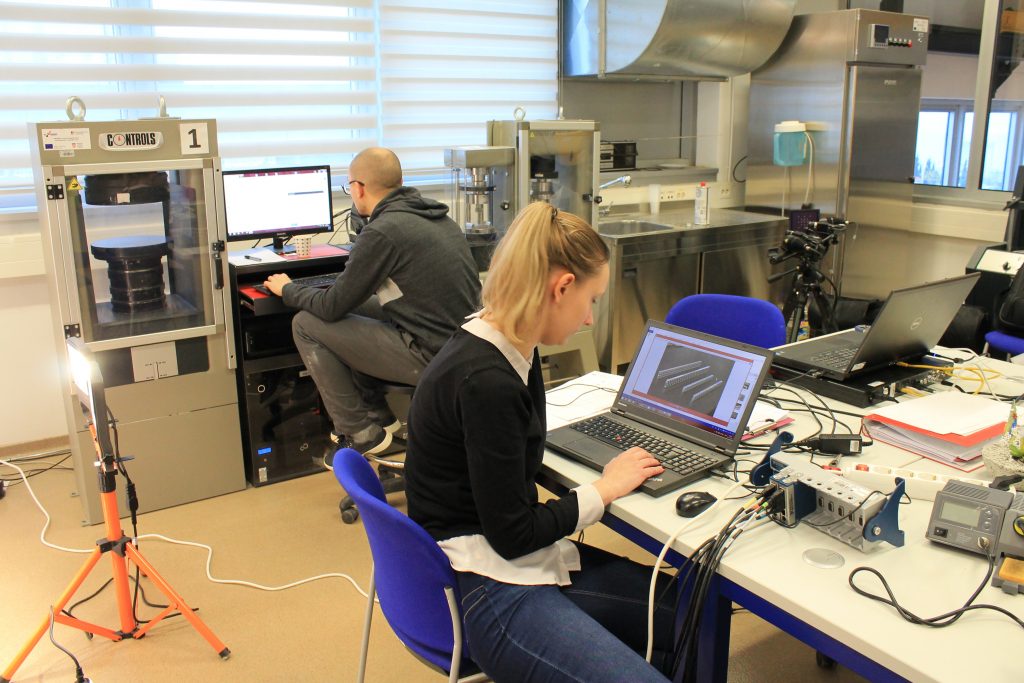
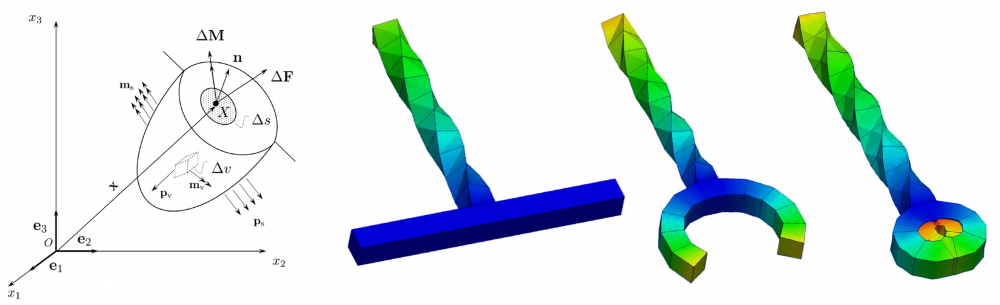
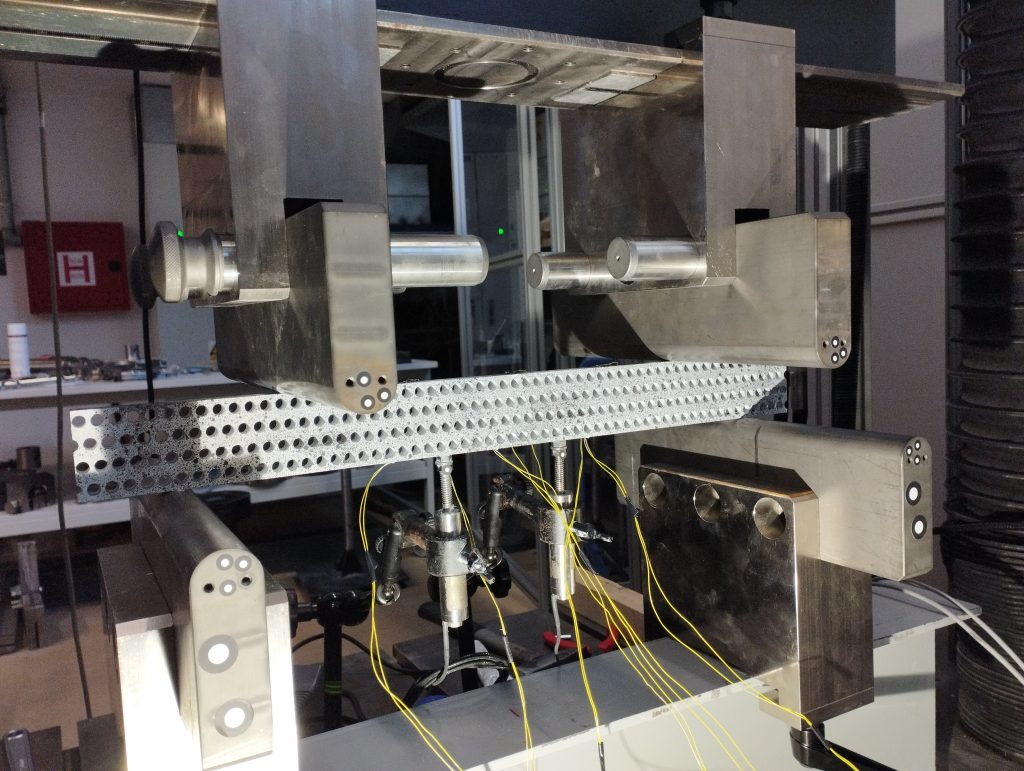
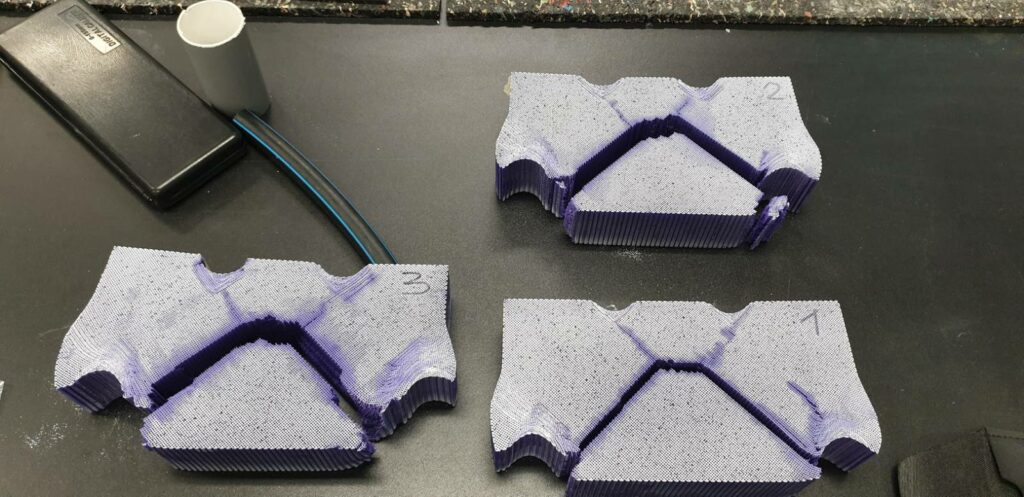
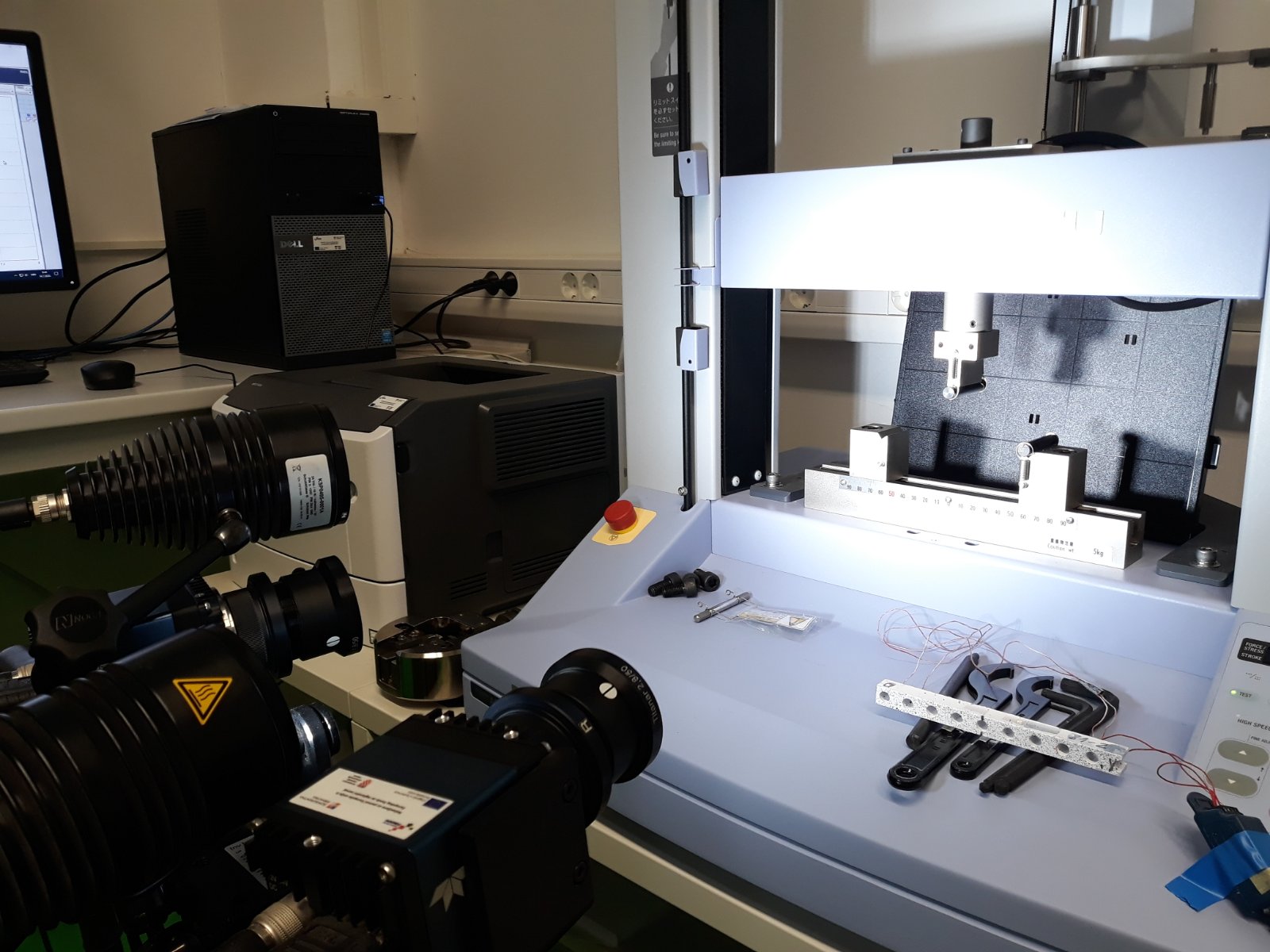
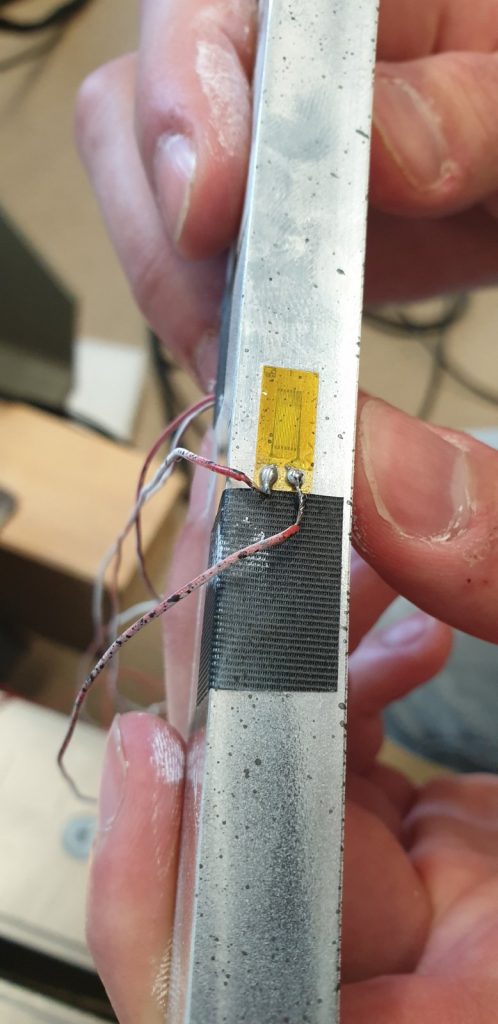
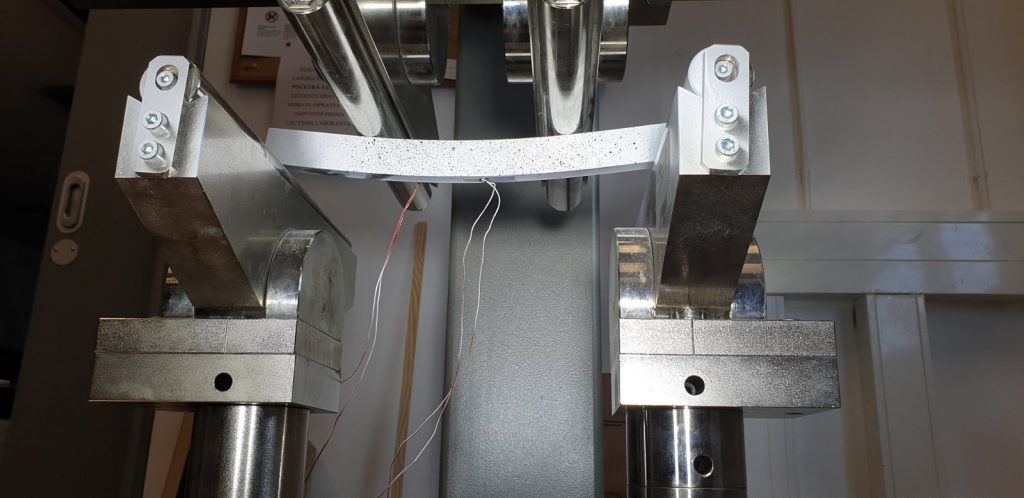
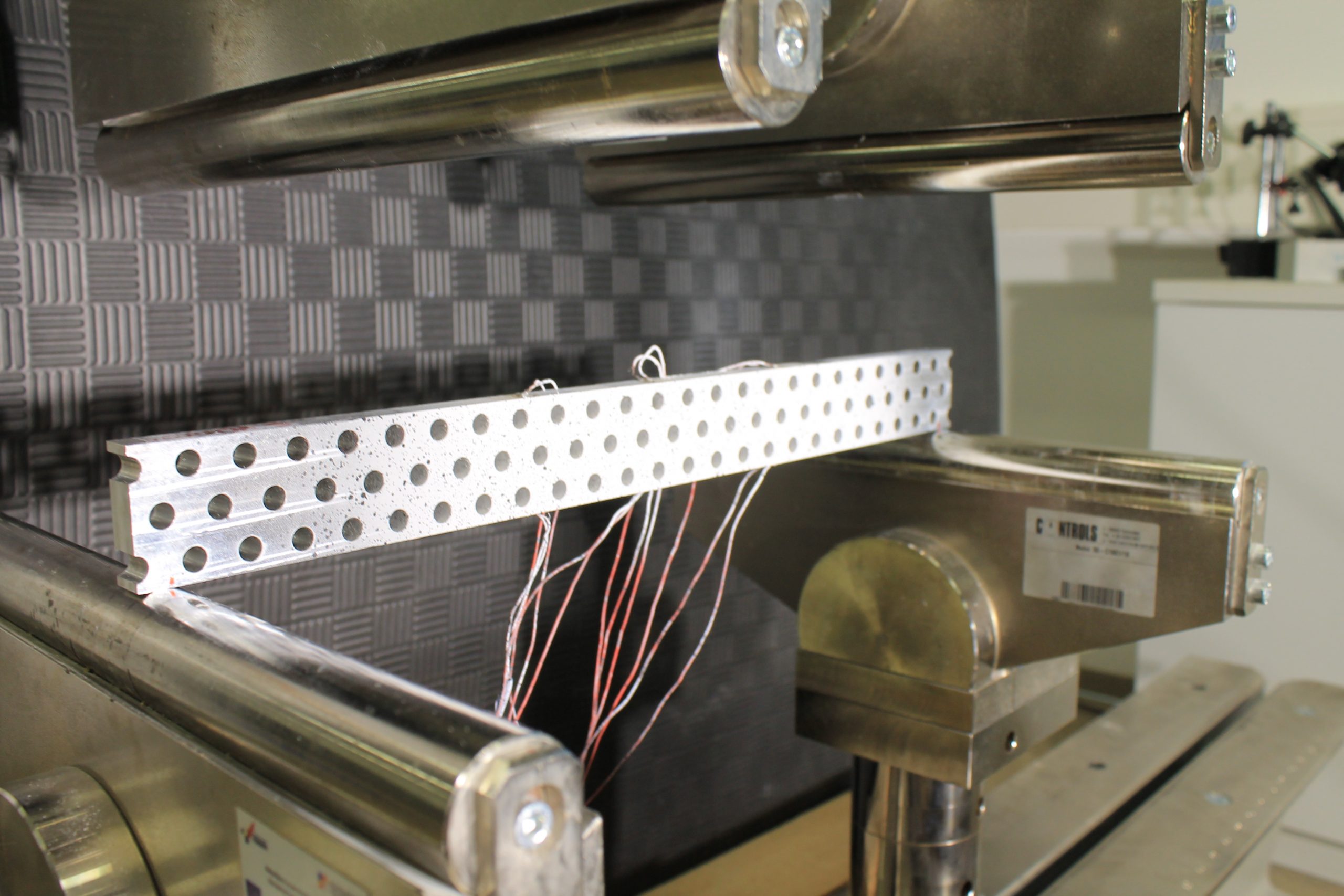
The sixth group of experiments was carried out from the 6th to the 8th of February 2023. Again, aluminium specimens with artificially created microstructure subjected to pure bending were examined. In this series of experiments, three specimens of the largest size (530×50,8×12,7 mm) with LMD microstructure were subjected to four-point bending.
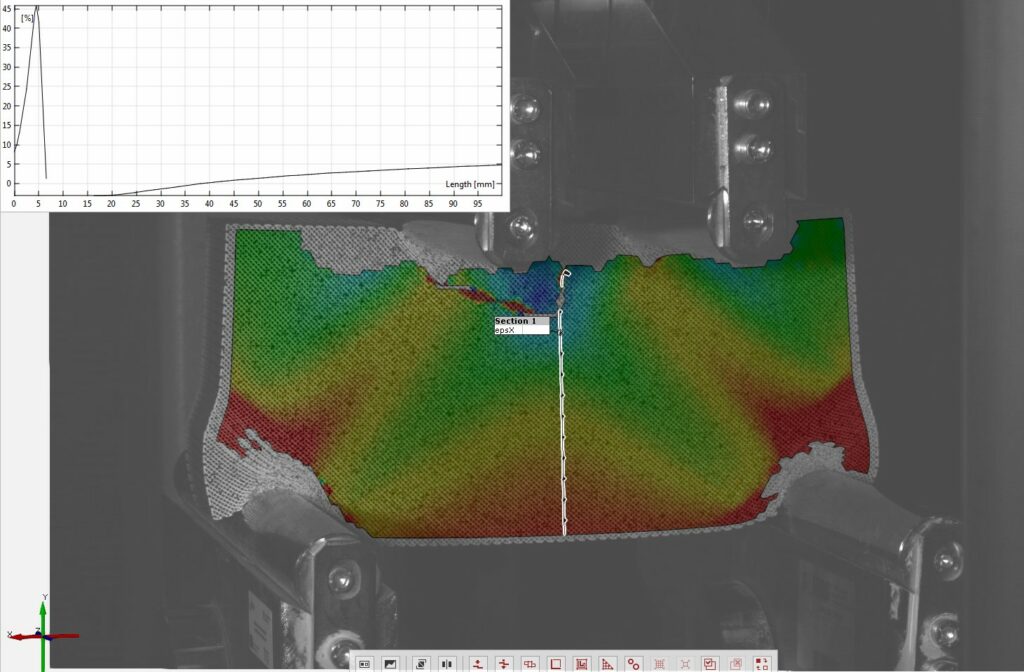
Each of the specimens was loaded with three different support placements, differing in span, but always symmetrical. The experiments were performed on the ZwickRoell Z600 universal testing machine with a 50 kN load cell. As before, our area of interest was in the strains on the top and bottom of the specimens, the values of which were obtained via strain gauges. Additionally, LVDTs measuring vertical displacement were set up symmetrically to the vertical axis. The same values were also measured by means of DIC via the GOM Aramis software.